Skin allergies: common causes, symptoms and treatment
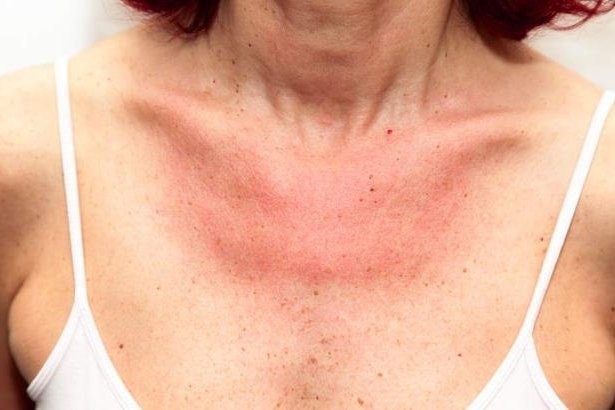
Skin allergies or skin allergies are reactions of the immune system to an allergen.
Table of Contents
Symptoms of skin allergies.
There are different types of symptoms that appear on the skin such as: erythema, itching, inflammation, increase in volume, rash, blisters, hives, peeling, the most common types being urticaria, atopic dermatitis and eczema.
Urticaria.
It is an alteration in the skin where there is a rash given by hives and hives that form on the entire body surface accompanied by intense itching.
The wheal corresponds to a raised area of the skin with redness and red edges that when pressed, its redness is attenuated. It may or may not be associated with angioedema.
It is estimated that one in five people has suffered an episode of hives. It occurs minutes after you have eaten a food or medicine and is often worse if you re-ingest what triggered the reaction.
Angioedema.
It corresponds to an affectation of the deep dermis that is characterized by increased volume in areas of lax areas of the skin such as lips, eyelids or scrotum and that can cause temporary deformity of the affected area, usually on the face.
Less frequently, inflammation of the tongue or glottis also occurs, which could make breathing difficult, requiring urgent medical attention.
It can be accompanied by urticaria; however, it also occurs in isolation without hives. It occurs as a consequence of the release of mediators that cause vasodilation and plasma extravasation. Depending on the responsible mediator, it may be histaminergic or bradykinergic. It is classified into drug, acquired angioedema, and hereditary angioedema.
Eczema.
It is a condition that initially gives rise to redness, itching and inflammation of the skin, later the lesions evolve into vesicles with liquid content inside. When these vesicles break, they form crusts when they dry, which corresponds to the acute form.
In the subacute form, the lesions persist over time and the skin becomes shiny and red, giving a varnish and peeling appearance. This process of chronification of lesions is called lichenification.
Atopic dermatitis.
It is a chronic inflammatory pathology of the skin, characterized by eczematous lesions, dry skin and intense itching. It is due to genetic and environmental causes. Atopic dermatitis is more common in children, it is estimated that its onset in adults is rare.
Studies have shown that during adolescence remission of symptoms occurs in 1/3 of cases and there is a decrease in the severity of symptoms.
This pathology affects the quality of life of patients, interfering with activities such as work, study and sleep cycles, it manifests itself with periods of exacerbations that alternate with asymptomatic periods.
This entity is related in 80% of the cases to atopic diseases such as bronchial asthma and rhinoconjunctivitis. Symptoms generally intensify at night and this leads to chronic scratching lesions with thickened and dry skin.
Common causes of skin allergies.
- Symptoms can be exacerbated by excessive heat or sweating, physical exercise, stress, respiratory tract infections.
- Insect bites, animal epithelia.
- Synthetic fabrics.
- Cosmetics such as soaps, creams and shampoo or detergents.
- Animal epithelia or plant spores.
- Food: In some cases, it is possible to detect an association of allergies with some foods, among which the most frequent are cow’s milk, eggs, soybeans and wheat flour. Food allergies are the most common types of allergies.
- Allergic drug reaction: The drugs that most frequently induce angioedema are angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). However, allergy to other types of drugs can occur.
- House dust or mites present on books and upholstery.
Treatment.
An essential part of the treatment is to detect and modify the causal or exacerbating factors of the outbreaks, these are allergens, infections and irritants of the skin.
In cases of urticaria, you should see a doctor for treatment in an emergency service. If the reaction recurs or is accompanied by respiratory symptoms and significant inflammation, the patient should be evaluated by an allergist.
The treatment of choice is the antihistamines for a period of at the least a week to prevent its recurrence; Depending on the severity of the case, treatment with corticosteroids is appropriate.
In atopic dermatitis it is recommended to keep the skin hydrated, control itching and inflammation with topical or oral medications.
Prevent sudden changes in temperature and humidity, physical exercise, stress, excessive sweating, the detergents used, the clothes should be washed with neutral soap, do not use fabric softener, use soap substitutes or soaps with neutral PH for daily cleaning.
Antihistamines are not always effective, there are other treatments such as phototherapy, topical corticosteroids, or topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs) (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus) that have fewer side effects.


