Why do warts bleed?
Warts have their own irrigation and innervation. They are contagious lesions, since they are caused by one of the subtypes of the human papillomavirus. Do you know why they bleed?

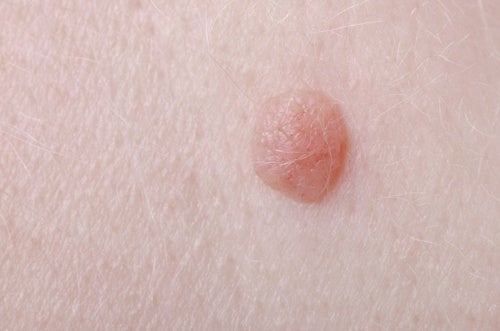
Warts are manifestations of the skin that are caused by the human papillomavirus. They are often asymptomatic and cause no problems beyond aesthetics. However, warts sometimes bleed or trigger some kind of pain.
While this is rare, it is often recommended to seek treatment to speed your recovery. Since they affect several layers of the skin, their removal can be complicated. In addition, they are contagious and can spread in various parts of the body.
Table of Contents
Symptoms of warts
A rough-textured bump is the main symptom of warts. Beyond this, it does not usually cause any discomfort. Only in certain cases, clinical manifestations include the following:
- Pruritus.
- Tightness or feeling of pressure.
- Pain, especially those located on the sole of the foot.
- Bleeding.
Causes of warts
Warts are caused by the human papillomaviruses (HPV), of which there are about 100 different types. Each serotype determines the location of the lesion in the body; hands, face, neck, armpits, feet, genitals, etc. In many cases, they resolve spontaneously, without the need for treatment.
The virus is able to enter the skin through wounds. Once it does this, it causes extra and rapid cell growth. The outermost layer of the skin becomes hard and thick, giving the wart body.
The American Academy of Dermatology affirms that the contagiousness is by direct contact with the injury, or, by sharing articles of personal use, like towels or razors.
Why do warts bleed?
Warts have their own blood supply, which generates abundant bleeding if they are tried to remove with inappropriate procedures. Specifically, they contain dermal papillae intertwined with vascular loops.
With the help of the dermatoscope, tortuous capillaries can be observed that generate a red dotted pattern on macroscopy, characteristic of the lesion. The wart also involves specialized nerve endings, which causes mild pain when handled.
Types of warts
Not all warts are the same. They are often classified according to the part of the body in which they appear. Also, its characteristics and symptoms may vary. What are the most common?
Plantar warts
They are often confused with corns. In this area its size is greater, since the sole of the foot must support the entire weight of the body. They do not grow exophytically, but do so inwards, when walking or standing. They are the most complicated to deal with due to their location.
Vulgar warts
They are usually located on the face, the back of the hands or on the cheeks. They are hard, rough and scaly growths to the touch. As detailed in a study in Public Health Association, it is one of the most common wart variants in children, with a 49% prevalence.
Flat warts
They are small, with a slight rise and little diameter. They do not have pigment; they remain with the same coloration of the surrounding skin. They are located on the face, with prevalence on the forehead, cheeks, hands, and forearms.
Genital warts
Some strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) cause warts in the genital area, including the vagina, penis, and anus. In fact, infection with this virus is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
Risk factor’s
Some people are more likely to develop warts. Furthermore, as its trigger is a virus, it is advisable to carry out an evaluation of the person’s immune system to rule out that it is compromised. Your risk factors include the following:
- People who handle or work with raw meat, for example in butchers or slaughterhouses.
- Children or adolescents who use popular showers, after playing sports or in swimming pools.
- People who have a family member with warts.
- Having immunodeficiencies: recipients of organ transplants or diseases such as AIDS.
Therapeutic options for warts
If the warts bleed, it is necessary to intervene as soon as possible to avoid complications. In fact, even if they do not present this symptom, there are those who prefer to give them a treatment so as not to suffer from their unsightly appearance. Procedures that can help include the following:
- Cryosurgery is used liquid nitrogen or solid carbon dioxide (also called dry ice) to freeze the tissue. It is a procedure that generates mild pain, but it is one of the most effective to remove warts. It must be done by a dermatologist, in several sessions every week.
- Topical medication: special acid-based formulations that slowly burn the wart. The product is applied every day and can cause slight irritation to the surrounding skin.
- Electrocoagulation: often leaves scars.
- Surgical removal: it is not used much, due to its low effectiveness and the risk of generating viral dissemination. It has a high percentage of recidivism.
- Laser: it is effective, it causes slight pain and can leave scars.
How to act if warts bleed?
When warts bleed, it is best to see a dermatologist for proper treatment. Trying to fix it at home can lead to complications, as the skin is damaged . Also, without timely intervention, it is difficult to get rid of this highly contagious problem.