What is and what are the symptoms of an enlarged liver
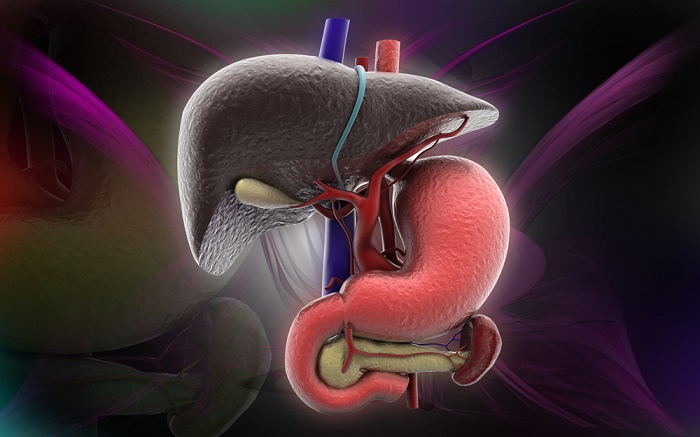
An enlarged liver, also called: hepatomegaly, or inflammation of the liver, occurs when the organ becomes larger than normal. It is a very serious condition, the inflammation can derive from a serious illness, like any of the hepatitis viruses.
Table of Contents
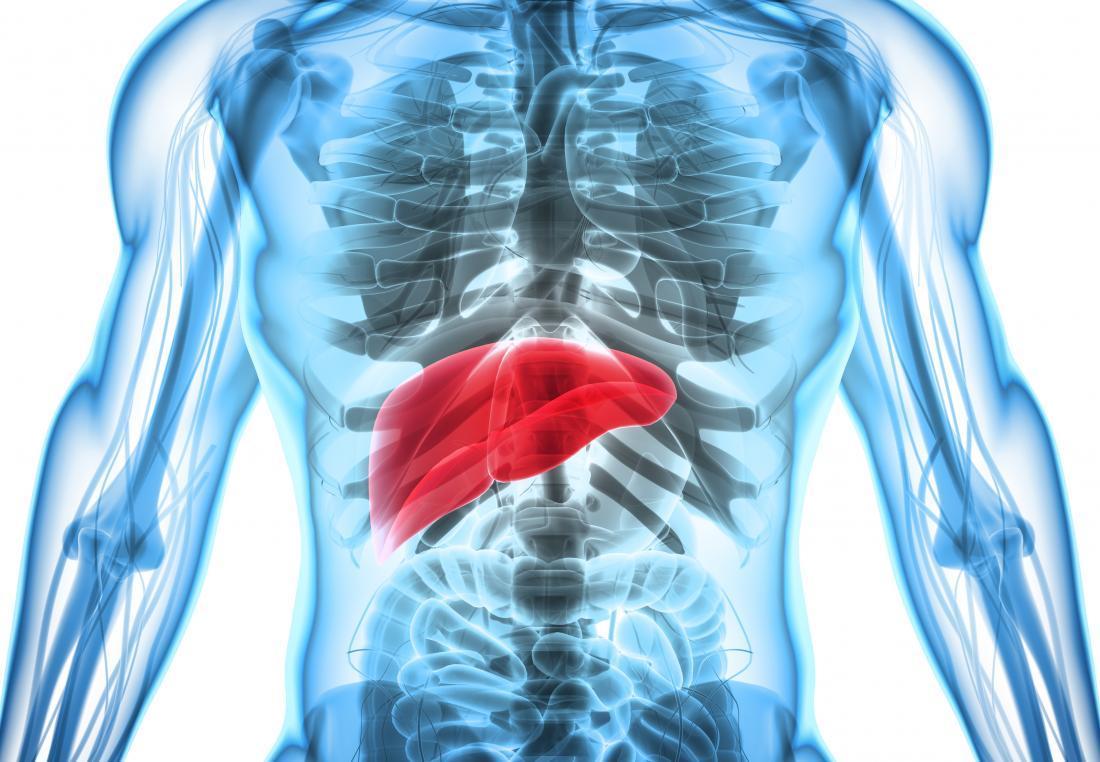
What is hepatomegaly or enlarged liver?
Unfortunately, it is not easy to identify such a condition, since in the early stages of liver inflammation, the symptoms that appear as liver failure progresses are hardly noticeable. However, there are some signs and symptoms that can help us know if we suffer from hepatomegaly or an enlarged liver.
The liver is one of the most important organs in our body as it is responsible for converting food into energy, eliminating toxins from the blood and regulating the levels of amino acids and fats, among many other functions. The liver is the largest of all organs, and inflammation can have serious consequences, so it is essential to take care of it and make sure it is working properly.
Since the liver performs many functions and is involved in many processes in our body, it is not surprising that the causes of liver inflammation are also varied.
The main factors that can cause hepatomegaly are:
- Excessive alcohol consumption. When the liver can no longer eliminate this substance, this can lead to inflammation of the organ.
- Infection with any of the hepatitis viruses, Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E. These always cause inflammation of the liver.
- Other viral infections such as infectious or bacterial mononucleosis or cytomegalovirus infections can cause inflammation of the liver.
- Drug poisoning will also activate liver inflammation.
- Other causes may be Niemann-Pick disease, primary biliary cirrhosis, Reye’s syndrome, or sarcoidosis or sclerosing cholangitis.
- The fatty liver is another anomaly that if left untreated, can also lead to inflammation of the liver.
- Finally, it should be noted that the appearance of a tumor, metastasis or leukemia can also cause hepatomegaly.
What are the symptoms of an enlarged liver?
During the first few days of liver inflammation, you probably won’t notice any symptoms in the body or oddities related to the liver. However, as you progress, these will become more and more apparent. In general, the initial symptoms of an enlarged liver are flu-like, feeling generally unwell, low-grade fever, muscle aches, and nausea.
Jaundice.
Over time the symptoms increase and intensify. Hepatomegaly usually causes jaundice, which is when the skin turns yellow (the eyes may also turn yellow). Vomiting and diarrhea are some of the most common symptoms of a swollen liver.
Being an inflammation, you will also likely notice that the abdomen feels slightly bulky in the first place and that over the days it will enlarge. Also, abdominal pain is another consequence of this condition.
Stool color.
The color of the stool is another factor that you should consider if you suspect that your liver is inflamed, this anomaly makes it lighter or even white. This is especially the case when the inflammation is caused by one of the hepatitis viruses. Remember that hepatitis is inflammation of the liver caused by a viral or bacterial infection. Because of this, urine can become darker than its normal color and sufferers can have a constant bitter taste in the mouth and bad breath.
These are the most common symptoms of an inflamed liver, but depending on the cause, few or even no symptoms may appear. Therefore, it is important to have annual exams, if you have any of the risk factors, such as chronically suffering from any of the aforementioned diseases, alcoholism or taking too much medication.
If you notice any of the aforementioned symptoms, you should see your doctor immediately to take the relevant tests and confirm or rule out liver inflammation. Remember that many of the causes are serious diseases, so you may have contracted one and do not know it yet.
To detect hepatomegaly, the doctor will first feel the area under the ribs, if the inflammation is severe, he or she will notify you immediately and then perform an abdominal X-ray to see if the liver is enlarged. If there is evidence of enlargement, the doctor can do an ultrasound to confirm. If confirmed, a CT scan will be performed to establish the causes of the inflammation, as well as liver function tests and an MRI of the abdomen to confirm the results of the scan.